
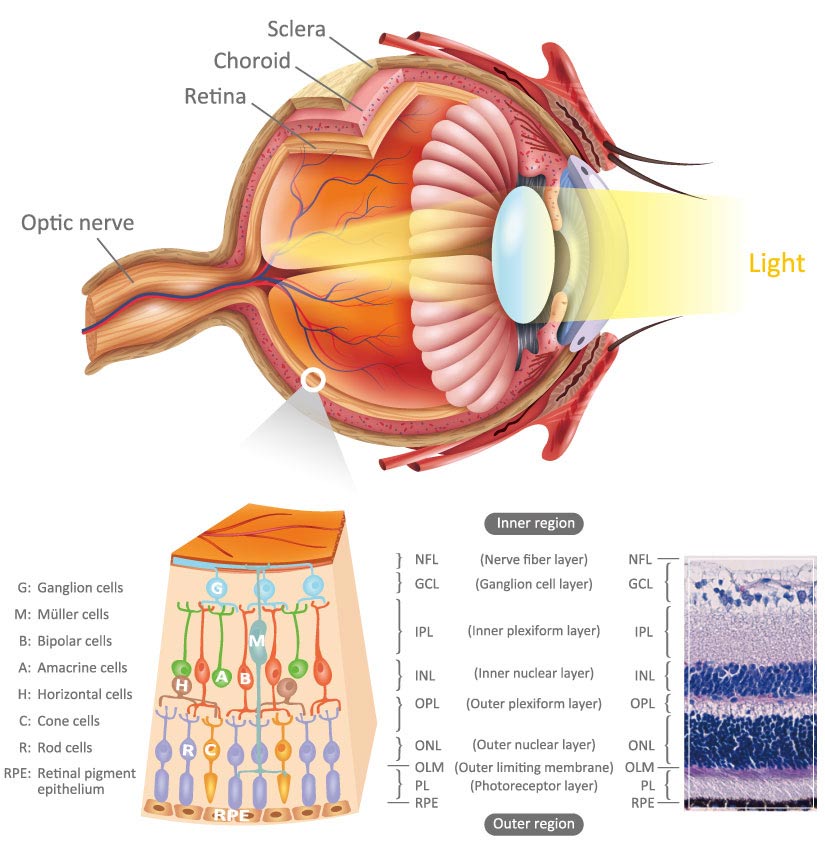
This technology has revolutionized the diagnosis and monitoring of eye diseases. This optic nerve carries the visual signals to the brain’s visual processing centers, allowing us to perceive the world around us.Ĭhanges in the thickness of the Rnfl are often used as a diagnostic marker for various eye diseases and conditions, such as glaucoma and optic neuritis.Īdvanced imaging techniques, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT), are used to non-invasively visualize and measure the thickness of the Rnfl. The Rnfl converges at the optic nerve head, where it forms the optic nerve. These bundles are responsible for transmitting visual information from the eye to the brain. Rnfl consists of bundles of nerve fibers that originate from the ganglion cells in the retina. This thickness variation is crucial in diagnosing eye conditions, as changes in thickness can signal potential issues. The Rnfl exhibits varying thickness across different regions of the retina. Before we delve into the intricacies of Rnfl’s structure and function, let us take a moment to appreciate the critical role it plays in the grand orchestra of vision. It is within the Rnfl that the initial processing of visual information begins. The significance of Rnfl cannot be overstated when discussing the visual system. The acronym Rnfl will be our guiding star throughout this article as we navigate the complex landscape of retinal anatomy. This delicate layer of nerve fibers is a fundamental component of the eye’s structure, specifically within the retina. In the realm of ophthalmology, Rnfl, which stands for Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer, is a term that holds immense importance. In this comprehensive article, we will delve deep into the intricate details of Rnfl, exploring its structure, function, and relevance in the realm of ophthalmology. Its significance in the visual process cannot be overstated, as it serves as the conduit through which visual information is transmitted from the eye to the brain. The Rnfl is a layer of nerve fibers that originates from the ganglion cells in the retina and forms the optic nerve. Rnfl, or Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer, is a critical component of the human eye’s anatomy that plays a pivotal role in vision.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
